Internet of Things (IoT): a connected and more agile world.
With 60% of the world's population connected to the Internet, we live in the era of interconnection, and this provides innumerable benefits but also challenges.
Imagine a world run entirely through the internet; this is the Internet of Things or IoT. The Internet of things is the process that allows connecting everyday physical elements to the network; from common household items like light bulbs to healthcare resources like medical devices; it also encompasses smart personal apparel and accessories and even smart city systems.
The term IoT refers to all systems of physical devices that receive and transfer data through wireless networks with minimal human intervention, which is possible thanks to the integration of computing devices in all kinds of objects. In simpler words, control lights through a Wi-Fi network, be aware of how many things are available in the refrigerator when you go home and thus be able to make the decision to buy or not what you need, count with a smart thermostat that receives location data from your smart car as you drive to adjust the temperature of your home before you arrive.
These are just a few common examples of what can be achieved with IoT, however, this advancement offers much more than simple household tasks. Its principle: everything is achieved without your intervention and even offers a better result than if you did it manually.
How does it work?
IoT devices connect with a process called M2M (machine to machine) in which two devices or machines communicate with each other using Wi-Fi connectivity, doing their work without the need for a human to intervene. This is necessarily done with specific sensors and chips that are arranged in the devices (for example, a smartphone usually has an ambient light sensor, gyroscope, etc.).
These connected devices generate a large amount of data that reaches an IoT platform that collects, processes and analyzes it. This information becomes relevant to the user because, thanks to it, conclusions can be drawn about their habits and preferences in order to make their lives easier. For example, if there is a fault with your car, you may receive a message reminding you to take it to the workshop.
An example of an IoT device is Amazon's Alexa smart speaker, which gathers information and interacts with other devices to give us the ability to control them through simple voice commands.
IoT examples.
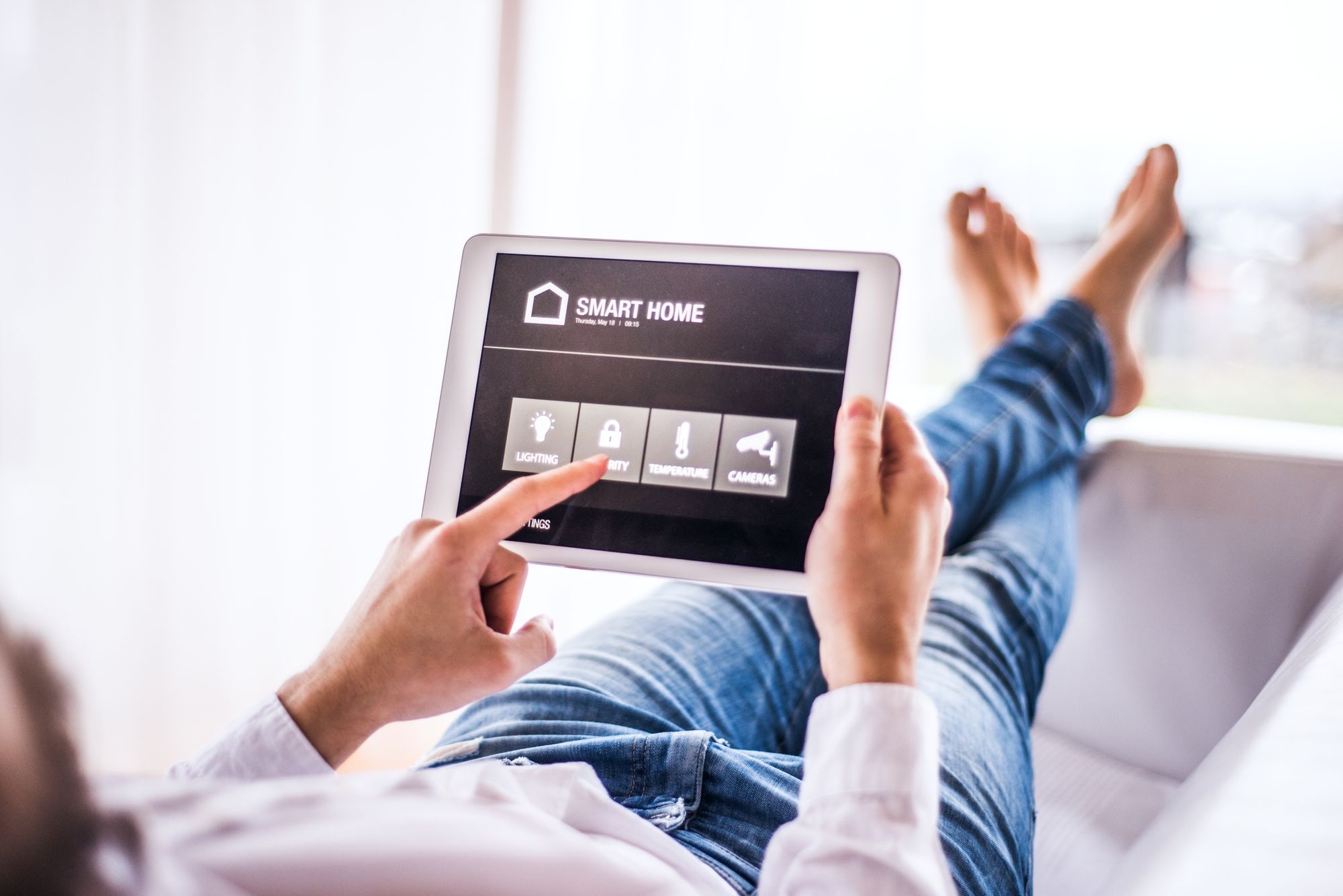
- Smart Homes: Many people are already intimately familiar with IoT networks in their own homes. As we explained earlier, home automation systems can be used to monitor and control things like lighting, HVAC, security systems, appliances, and more (even from afar).

- Smart cities: According to the Smart City Index (SCI), a smart city is "an urban environment that applies technology to enhance the benefits and reduce the shortcomings of urbanization." The increase in population, traffic congestion and the aging of infrastructures are some of the challenges that the IoT is helping to address. Using sensors, meters, and other IoT devices, urban planners can monitor and collect data to proactively address issues. For example, sensors placed in drains can detect water levels and automate actions to help prevent flooding when levels get too high.
- Enterprise IoT: Enterprise IoT solutions enable you to improve current business models and build new relationships with customers and partners. However, its implementation presents certain challenges. The volume of data generated by a system of smart devices can become overwhelming. Integrating big data into existing systems and setting up analytics to use that information can be challenging.
- IoT in agriculture: IoT has revolutionized the agricultural sector in several ways, such as the use of humidity sensors. When they are installed in the fields, farmers get more accurate data to schedule irrigation periods. In addition, they can connect them to the IoT applications that control the irrigation machinery, which is automatically activated based on the data generated by the sensors.
- IoT in logistics and transportation: One of the earliest implementations of IoT in the logistics and transportation industry involved tagging shipping containers with radio frequency identification (RFID) devices. These tags store data that can be picked up via radio waves, allowing logistics companies to track container movements at certain RFID-enabled checkpoints, such as warehouses or terminals. Thanks to advances in the IoT, battery-powered tracking devices have been developed that continuously transfer data to IoT applications without the need for on-premises readers, making it possible for companies to analyze shipment information instantly in each section of the supply chain.
- IoT in medicine: the use of smart devices based on the technology of the internet of things has brought multiple benefits to medicine. Among them we can highlight:
- Increased mobility and motivation of staff in the performance of their duties.
- Streamlining the process of patient information.
- The risk of errors in diagnoses and treatments is minimized since automation in turn reduces human intervention.
- Increased profitability of treatments.
Smart monitoring devices are the most widespread Internet of Things applications in the medical field. Likewise, the IoT is responsible for the maintenance management of equipment in hospitals and clinics and, through sophisticated sensors, tracks the health of seriously ill patients. The devices control the patient's health conditions, from the moment they enter the medical center and throughout their stay there, timely updating the user's information autonomously.
As time goes on, we are seeing an increasingly fluid interaction between technology and the human experience. The implications of this are vast and have the potential to change the way we approach some of our most fundamental activities and institutions such as workplaces, surgical and medical care, real estate, shopping, travel and general human relations. The possibilities offered by the Internet of Things are innumerable and are only limited by our imagination.
If you liked this article, subscribe to our blog.
Remember that you can find us on Instagram, Facebook and Twitter as @esauriook
On LinkedIn as e•Saurio

